When you send an email and it bounces back with a message like “554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy,” it means your email didn’t pass the receiving server’s authentication checks. This isn’t just a random failure; it’s a DMARC permanent error that signals something’s wrong with your domain’s DNS records.
In simpler terms, the error happens because your email authentication setup, DMARC, SPF, or DKIM, is either broken or misaligned. The receiving mail server checks your DMARC policy and finds that the message doesn’t meet the required authentication rules. Most of the time, this is caused by small syntax errors in DNS records, missing authentication entries, or strict enforcement settings under DMARC.
In this article, we’ll explain what the error means, what causes it, and how to troubleshoot it step-by-step.
Key Takeaways
- The 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy means the recipient’s server rejected your message due to authentication or alignment issues.
- A DMARC permanent error isn’t caused by spam filters, it’s a result of incorrect or incomplete DNS records.
- Common causes include missing semicolons, invalid syntax, or SPF/DKIM misalignment.
- Fixing it requires validating your DNS configuration and ensuring your SPF and DKIM records align with your From domain.
- Tools like DMARC, SPF, and DNS record analyzers can help identify errors and confirm that your records meet DMARC requirements.
Common Causes of 554 5.7.5 Permanent Errors
When a DMARC check fails, email servers return specific error messages to show what went wrong. These messages may look technical, but understanding them helps you pinpoint the issue faster. Below are some examples you might see when your domain runs into a DMARC permanent error:
- 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy
- Remote server returned ‘554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy’
- 451 4.7.5 temporary error evaluating DMARC policy
- Permanent error evaluating DMARC policy
- Email rejected per DMARC policy
1. What the Error Code Means
SMTP error codes like 554 indicate that the email transaction has failed and will not attempt again. This means the message was fully rejected due to a DMARC rule violation.
In contrast, codes like 451 show temporary problems, often DNS lookup delays or timeout issues. Temporary errors may resolve automatically once the DNS record becomes available or propagates correctly.
2. Real-World Examples of DMARC Failures
Here are a few real-world rejection strings you might see when a DMARC permanent error occurs.554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy: a generic message seen across multiple mail providers.
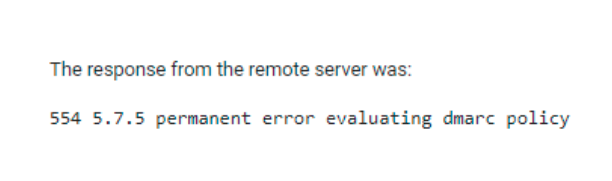
521 5.2.1: This message failed DMARC evaluation and is being refused due to the provided DMARC policy
550 5.7.1: Unauthenticated email from example.com is not accepted due to the domain’s DMARC policy
Important Notes:
You might also see phrases like “email rejected per DMARC policy” or “unauthenticated email not accepted.” The exact text depends on how the receiving Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) handles authentication failures.
Also, not every 550 or 554 error automatically points to DMARC. Sometimes, generic 550/554 rejections relate to spam filters, blacklists (RBL hits), or rate-limiting issues unrelated to DMARC itself.
Why DMARC Permanent Errors (554 5.7.5) Happen
A 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy happens when your email authentication setup fails one or more checks during delivery. In simple terms, the receiving mail server looks at your message, compares it to your domain’s DMARC, SPF, and DKIM policies, and finds that something doesn’t line up.
Below are the most common reasons this happens. Each one can trigger a DMARC permanent error if not configured correctly.
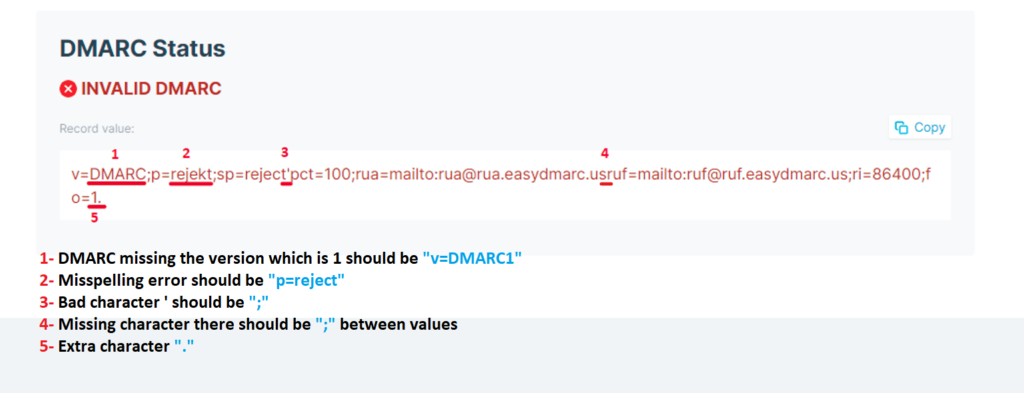
1. Invalid DNS Syntax
Validate DNS Records
Your domain’s DNS records are like a rulebook for other servers. Even a small typo in those rules can break authentication.
Common syntax mistakes include:
- Missing or extra semicolons between tags
- Quotation marks in the wrong place
- Using colons instead of semicolons
- Misspelled tags or unsupported parameters
When this happens, the mail server can’t read your DMARC record properly. Since the policy can’t be interpreted, the server may fail the DMARC check and handle the message based on its own rules, potentially rejecting the email.
2. Policy Enforced but Not Aligned
If your domain has a DMARC policy set to p=quarantine or p=reject, but your SPF or DKIM results don’t align with the From domain, the message will fail DMARC.
Alignment means the domain listed in your email’s From header must match the domain authenticated by SPF or DKIM.
For example:
- From: [email protected]
- DKIM signed by: mailer.example.net
Even if DKIM passes, it’s not aligned because the signing domain (mailer.example.net) doesn’t match your From domain (example.com). DMARC will then fail and cause a permanent error evaluating the DMARC policy.
3. SPF Issues
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) tells receiving mail servers which IP addresses or services are allowed to send mail for your domain. If this record is incomplete or poorly formatted, it often leads to a DMARC permanent error.
Typical SPF issues include:
- Missing authorized IP addresses or hostnames
- Ending your SPF record with ?all (neutral) instead of ~all (soft fail) or -all (hard fail)
- Too many DNS lookups (more than 10), which triggers a “permerror”, short for permanent error
- Syntax problems, such as missing spaces or colons
These problems make your SPF fail, which means DMARC can’t verify that the message truly came from your domain.
4. DKIM Issues
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a digital signature to your emails. When this setup fails, the recipient can’t confirm that the message was truly sent by your domain, another reason for a 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy.
Common DKIM-related causes include:
- DKIM selector not published in DNS
- Missing or invalid TXT key
- The d= domain in the DKIM signature doesn’t match the From domain
- Corrupted or outdated private/public key pair
If DKIM fails, and SPF is also misaligned or fails authentication, DMARC enforcement will reject the message completely.
Troubleshooting Permanent Error Evaluating DMARC Policy
If you’re receiving the 554 5.7.5 permanent error, follow these steps to validate your DNS records and restore proper alignment.
1. Validate DNS Records
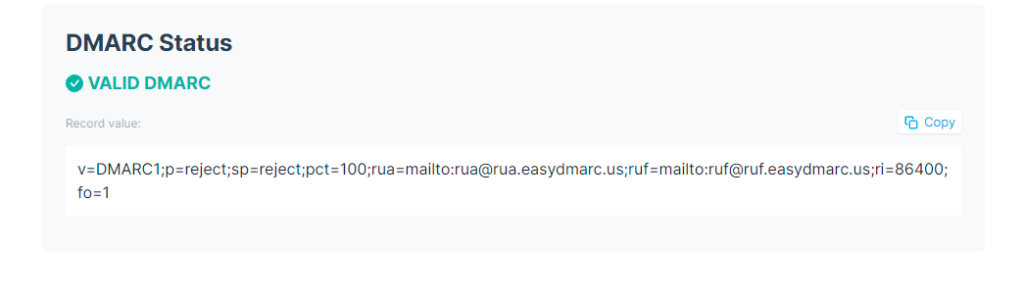
Every DMARC record must meet three basic rules:
- It must begin with v=DMARC1.
- The policy (p=) must be one of these: none, quarantine, or reject.
- Tags must be separated by semicolons (;), not commas or colons.
Avoid common mistakes like missing semicolons or extra spaces. Even small errors can make the record unreadable.
Use your DMARC lookup tool to check that your record is properly formatted and visible in DNS.
2. SPF Validation
- Make sure all authorized sending IPs and email services (like Google Workspace, Outlook, or Mailchimp) are included in your SPF record.
- End your record with ~all or -all, not ?all.
- Avoid more than 10 DNS lookups to prevent SPF “permerror.”
- Run an SPF lookup tool or the EasySPF feature to confirm everything is correct.
3. DKIM Validation
- Verify that your DKIM selector record exists in DNS.
- Ensure the TXT key is valid and not truncated.
- Confirm that the domain listed in the d= tag aligns with your From domain.
- Use our DKIM lookup tool to confirm that your key is valid and active.
4. Check Alignment
DMARC only passes when both SPF and DKIM pass and align with the From domain.
SPF = pass (but MAIL FROM = mailer.example.net, not aligned with example.com)
DKIM = fail
DMARC = fail → 554/550 rejection
SPF = pass and aligned
DKIM = pass and aligned
DMARC = pass → message delivered
5. Test and Monitor
Once your records look correct, run a live test. Use EasyDMARC’s Header Analyzer to review your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC results on real emails.
It’s also important to monitor your aggregate DMARC reports. These reports show who’s sending mail on your behalf and whether those messages are passing authentication. Regular monitoring helps you spot failing services, unauthorized senders, or shadow IT systems before they affect delivery.
Final Thoughts: Understanding and Fixing DMARC Permanent Errors
A 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy can look intimidating, but it’s really just a signal that your domain’s authentication system is doing what it’s meant to do: protecting you. The error appears when DMARC enforcement detects a misconfiguration in your DNS records or finds that SPF or DKIM alignment doesn’t match your From domain.
The fix usually involves checking your DNS syntax, updating SPF and DKIM records, and making sure both align with your domain. Once these are corrected, your messages will start passing DMARC checks and reach inboxes without issue. Use EasyDMARC’s lookup and analysis tools to validate records and monitor reports, or reach out to EasyDMARC Support if you need expert help resolving DNS or alignment errors quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions
It means your email was rejected because it didn’t meet your domain’s DMARC authentication rules. Usually, SPF or DKIM didn’t align correctly with your From domain.
Check your DMARC, SPF, and DKIM records for syntax errors or alignment issues. Make sure your DMARC record starts with v=DMARC1, uses valid tags, and that SPF/DKIM align with your sending domain.
No, the 554 5.7.5 permanent error evaluating DMARC policy isn’t caused by Gmail or Outlook. It occurs due to misconfigurations in your own DNS or email authentication setup.
A temporary error (451) means the mail server faced a short-term issue, like a DNS timeout. A permanent error (554) means the configuration itself is wrong, so the message is rejected until it’s fixed.





