Recently, Microsoft made significant changes to their DMARC policy handling, which is of utmost importance.
For your information, DMARC is a standard designed to prevent spoofing by verifying the identity of email senders. If an email fails DMARC validation, it raises suspicions that the sender may not be genuine, potentially indicating fraudulent content. The ‘p=’ value within a DMARC record indicates the sender’s policy for their domain, dictating the receiver’s actions when an email fails DMARC validation. The policy can have three values: none, quarantine, and reject. The DMARC “reject” policy (p=reject) is the strictest level of the policy, and it instructs the receiver to outright reject any emails that fail the DMARC check.
Previously, Microsoft was not adhering to DMARC policies as expected, allowing emails that failed DMARC checks to bypass rejections set in the DMARC policy ‘p=reject.’ Consequently, if users hadn’t activated the rule to reject non-authenticated emails received from domains protected with a DMARC “reject” policy, they would still receive these non-authenticated emails instead of them being rejected.
Microsoft has recently made significant updates to their DMARC policy handling, impacting both consumer and enterprise customers. For their consumer services (live.com / outlook.com / hotmail.com), they have now aligned their DMARC policy handling with the sender’s DMARC policy. This means that if an email fails DMARC validation and the sender’s policy is set to p=reject, Microsoft will reject the email. This change aims to enhance email security and protect users from potentially fraudulent or spoofed emails.
For emails that fail DMARC validation with a reject policy and the corresponding action is taken on the message, the sender will receive a non-delivery report (NDR) containing the following message:
“550 5.7.509: Access denied, sending domain example.com does not pass DMARC verification and has a DMARC policy of reject”.
Microsoft has introduced new flexibility for their Enterprise customers regarding the handling of emails that fail DMARC validation. Now, customers have the option to choose different actions based on the policy set by the domain owner, such as p=reject or p=quarantine.
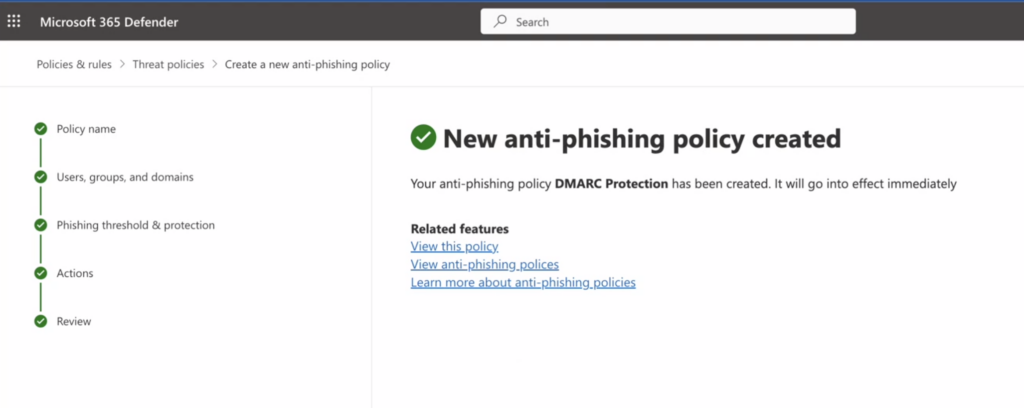
To establish a new Anti-Phishing policy and ensure that you honor the DMARC policy as expected, kindly adhere to the following instructions:
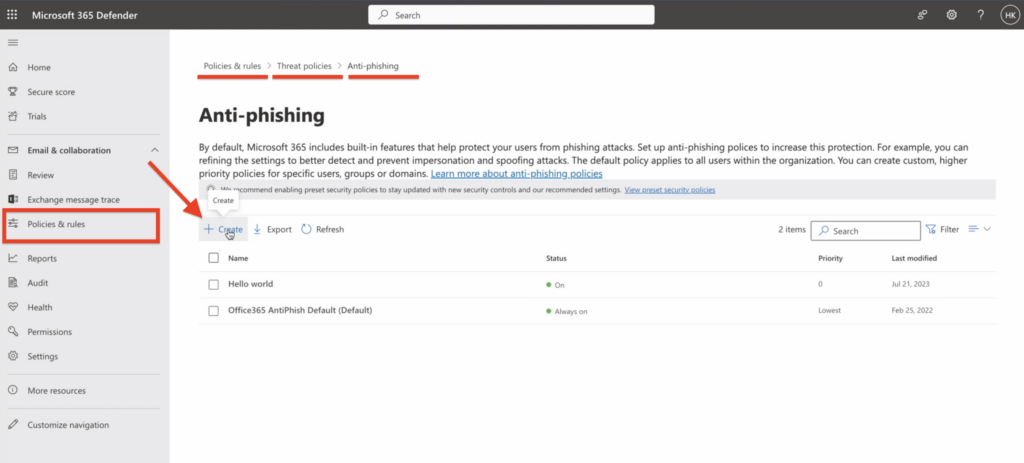
Visit the Microsoft 365 Defender portal at https://security.microsoft.com.
Navigate to “Email & Collaboration” > “Policies & Rules” > “Threat policies” > “Anti-phishing” within the “Policies” section.
If you prefer to access the Anti-phishing page directly, you can use the URL: https://security.microsoft.com/antiphishing.
- On the Anti-phishing page, select
Create to open the new anti-phishing policy wizard.
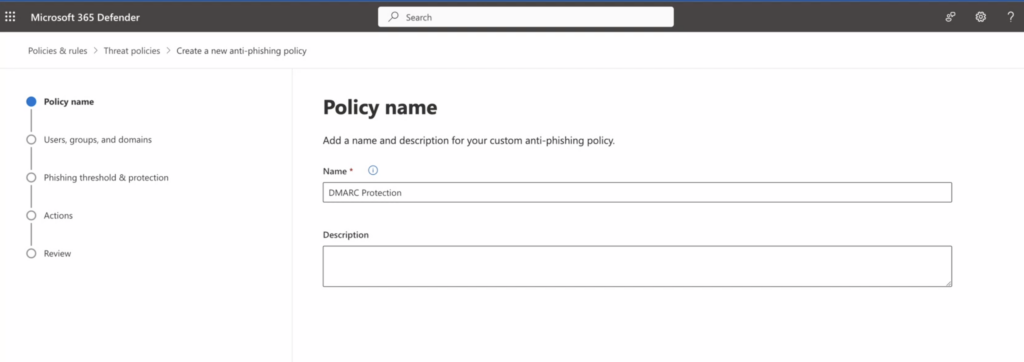
2. On the “Policy name” page enter a unique, descriptive name for the policy and click “Next”.
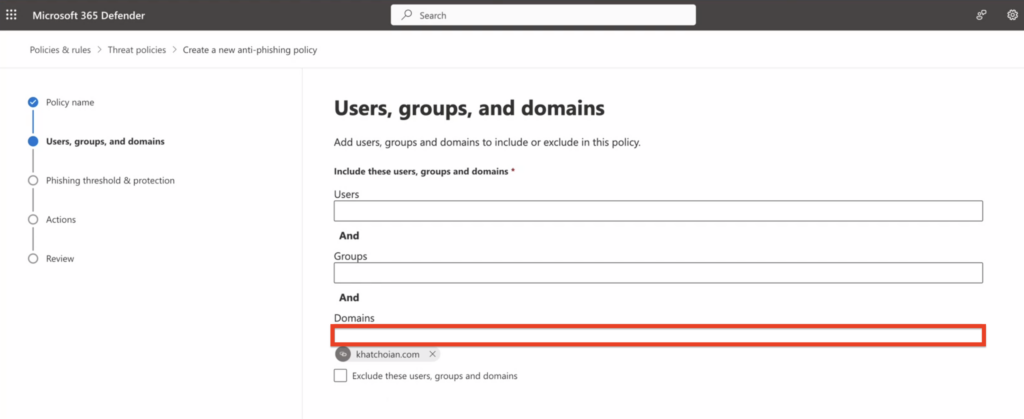
3. On the Users, groups, and domains page, mention the domain/s the policy applies to, and click on “Next.”
4. Ensure that “Enable Spoof Intelligence” is activated, then proceed by clicking “Next.”
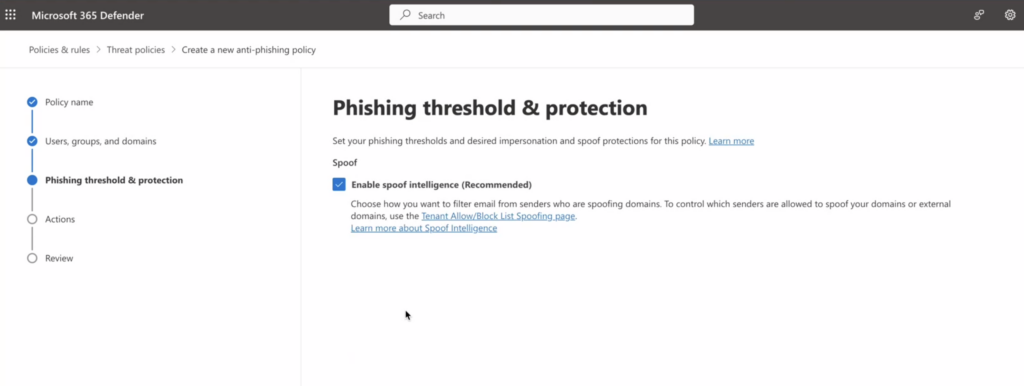
5. Enable the option “Honor DMARC record policy when the message is identified as spoof.”
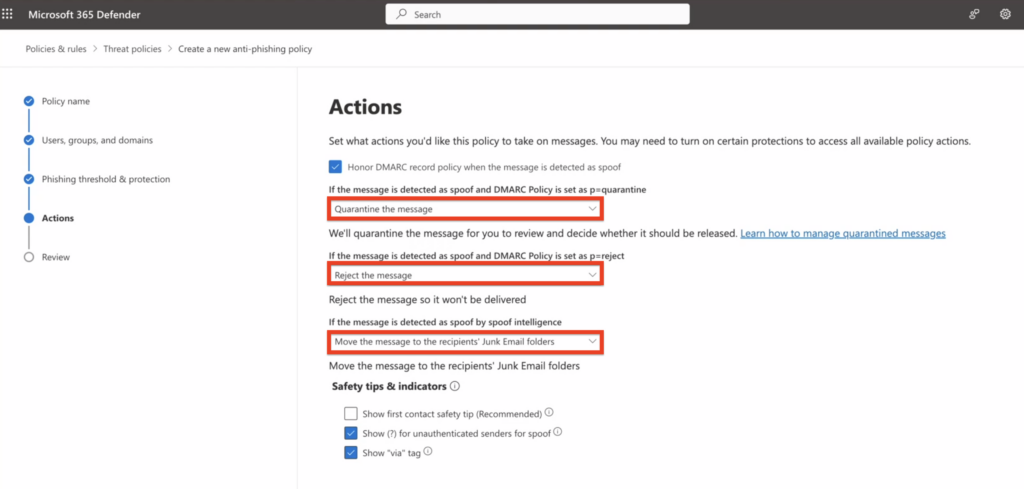
– If the message is detected as spoof and DMARC Policy is set as p=quarantine, select “Quarantine the message”
– If the message is detected as spoof and DMARC Policy is set as p=reject, select “Reject the message”
– If the message is detected as spoof by spoof intelligence, select “Move the message to the recipients’ Junk Email folders”
6. Finally, submit the policy.