DMARC Record Generator
Generate DMARC Records in a few clicks and use it in your DNS
What is a DMARC Record?
A DMARC record is a TXT entry in your domain’s DNS that defines how incoming mail servers should handle messages that fail authentication checks. It acts as a set of instructions, guiding servers to either reject, quarantine, or accept emails that don’t meet verification criteria.
Having a DMARC record means domain owners can track email activity and identify unauthorized use through DMARC reports. Without a DMARC record, receiving servers don’t have clear instructions on how to handle unverified emails, which increases the risk of phishing and domain spoofing.
Here is an example of a published DMARC Record:
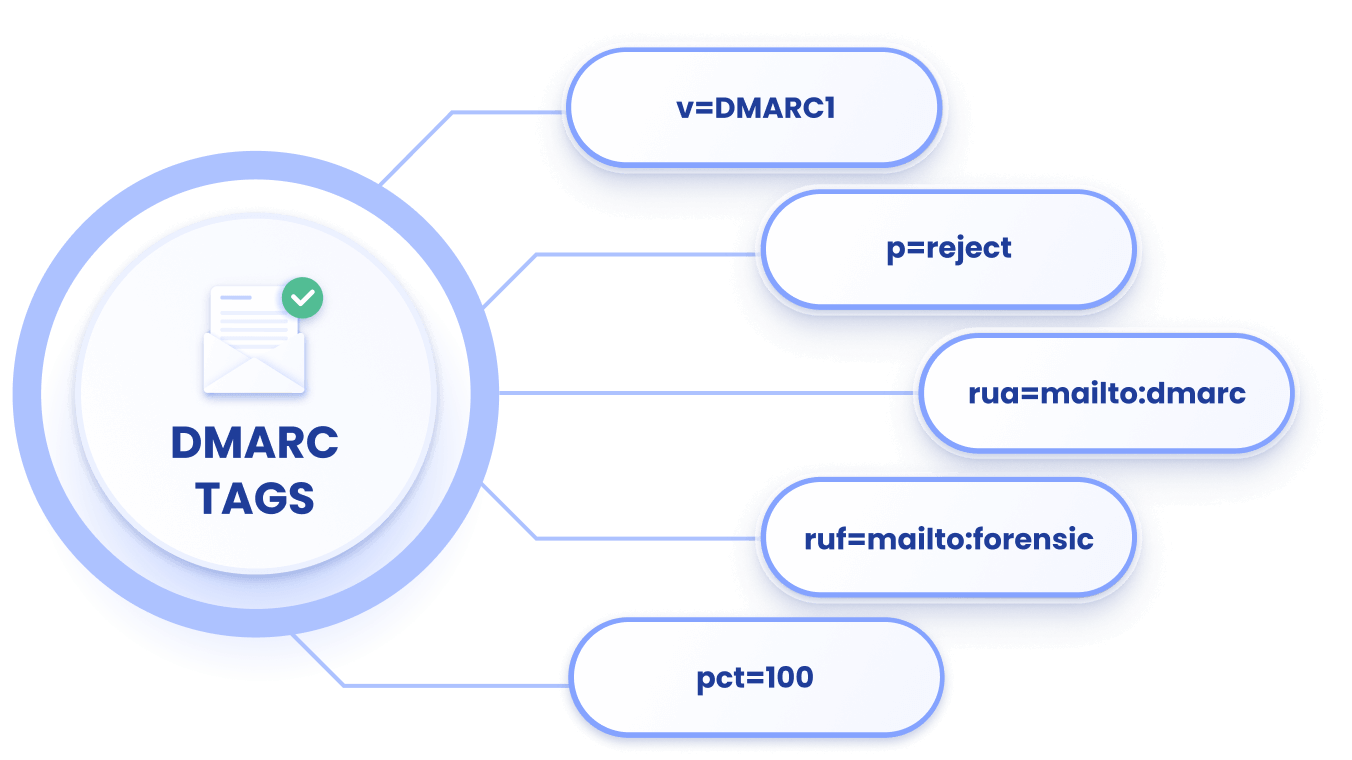
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@easydmarc.com
In this example, ‘v=DMARC1’ indicates the version of DMARC being used,which is usually DMARC 1, while ‘p=none’ refers to the domain’s DMARC policy and tells receiving servers what to do with the message if it fails a DMARC check. The email address given is where DMARC reports will be sent to.
How to Create a DMARC Record
If you’re using EasyDMARC’s DMARC Record Generator tool, the process should be a breeze:
- Input your domain and select the policy you’d like to apply (More about policies here)
- Add the email addresses you wish to use for DMARC reporting (Aggregate and Failure)
- Click "Generate"
Please note that other fields in our tool are for finetuning optional or default tags. You can skip them and still have a perfectly usable DMARC record.
How to Generate Your Valid DMARC Record
Having a valid DMARC record in your DNS can be the difference between a protected email infrastructure and having to pay a ransom to hackers. While you can create a DMARC record manually (if you know the right syntax), generating one with a DMARC record creator is much quicker, easier, and error-free. EasyDMARC’s DMARC Record Generator is the quickest way to generate a DMARC record with the right policy, reporting domains, and any optional tags you require.
EasyDMARC’s DMARC creator is helpful if your DMARC checker results show that you’re missing the record or it contains any errors. It’s also irreplaceable for record updates during a policy change or adding more report recipients. Once you generate the DMARC record, you’re just a step away from monitoring your email environment. Adding the record to your DNS allows you to analyze your domain infrastructure and resolve any issues one by one.

What Is a DMARC Record Generator?
EasyDMARC’s DMARC Record Generator allows you to create a valid DMARC Record in a few clicks. The generated syntax will meet all your specifications and be ready to publish in your DNS.
How to implement a DMARC record for your domain?
Once the record has been generated, copy it and go to your domain’s DNS zone. Add a new TXT or CNAME record, then paste the provided DMARC record.
Note: Most DNS providers (e.g. GoDaddy) automatically include the domain name in the Host/Name field, so you only need to enter _dmarc.
What’s the DMARC record format?
TXT is the accepted DMARC record format if you’re dealing with it manually.
When using EasyDMARC’s Managed DMARC solution, the type of DMARC record that should be added to the DNS is a CNAME record. A CNAME (canonical name) record is a DNS record that can create an alias for the domain and allow traffic for the domain name to be redirected elsewhere.
What is DMARC domain alignment?
Domain alignment is the core DMARC concept. Alignment happens when the domain name in the email's "From" header matches the sender's email domain. As a result, DMARC passes, indicating that it was a legitimate email.
DMARC domain alignment helps protect against spoofing, impersonation attacks, business email compromise, and phishing.
How does DMARC work with subdomains?
Subdomains inherit DMARC settings from the parent domain unless specified otherwise.
For example, if the parent domain has a ‘reject’ policy, the subdomain will inherit it. However, if you configure the subdomain separately, the system will not override your manual DMARC settings.
Can I add a DMARC record without SPF or DKIM?
You can add the record, but it won’t function properly.
DMARC is based on SPF and DKIM. For it to pass, an email must pass SPF authentication and SPF alignment and/or DKIM authentication and DKIM alignment. If both are missing, DMARC will fail.

