DMARC Record Lookup
Check DMARC Records to find any security issues and fix them.
Reliably Authentic Emails Every Time with DMARC Record Checker
EasyDMARC’s DMARC Record Checker is the most powerful and user-friendly DMARC diagnostic tool for DMARC validation and record testing. Our DMARC checker tool can easily look up DMARC records to test authenticity and ensure correct configuration.
After using our DMARC lookup tool to compile any DMARC record issues, you’ll need a good platform to help you solve them, and that’s where Easy DMARC has you covered. Our platform provides all the necessary tools and action plans to achieve security compliance. Try EasyDMARC’s DMARC checker today, and find out how we can help make your email authentication easy, secure, and fast.
What Is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an email authentication protocol that protects domains from unauthorized use, such as phishing and spoofing attacks. By implementing a DMARC record, domain owners can specify how receiving email servers should handle messages that fail SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) checks.
DMARC helps ensure legitimate emails are delivered while providing detailed reports to monitor and strengthen email security. It’s an essential step for safeguarding brand reputation and enhancing email deliverability.
Why Use EasyDMARC For DMARC Lookups?
When it comes to DMARC lookups, EasyDMARC stands out as a trusted solution.
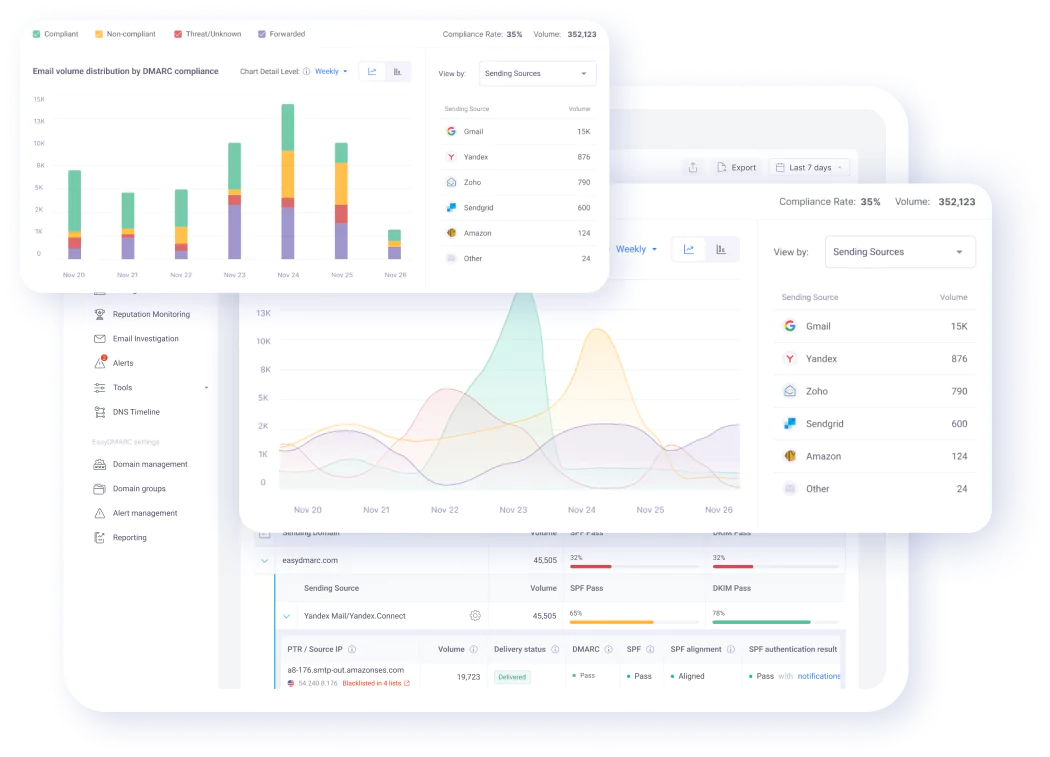
Comprehensive Reporting and Analysis
- Gain detailed insights into email authentication results
- Identify spoofing attempts and misconfigurations with ease
- View clear visualizations and in-depth reports that help you understand your email ecosystem
User-Friendly
Interface
- Intuitive dashboard designed for all skill levels
- Effortlessly navigate, configure, and analyze your DMARC data
- Simplified setup process with helpful guides and prompts
Enhanced Email
Security
- Protect your brand from phishing, spoofing, and impersonation attacks
- Ensure only authorized entities can send emails on your behalf
- Receive real-time alerts to stay ahead of potential threats
Advanced DNS Record Checking
- Validate your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records with a single click
- Detect misconfigurations that could weaken your email security
- Get recommendations to optimize your DNS records for maximum protection
Tailored Features for Every Need
- MSP and Enterprise-friendly tools to manage multiple domains
- Scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes
- Ongoing updates to keep you ahead of emerging threats
Trusted by Thousands of Organizations
- Proven results with clients in diverse industries
- A strong reputation for reliability and efficiency in email security
EasyDMARC Has Everything You Need For Secure Servers
Discover a suite of powerful tools designed to enhance your email security.
Discover these and other best-in-class features
by signing up for a 14-day free trial.
Start your Free TrialWhat is a DMARC Record?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is an email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol. You generate the record syntax and add it to the DNS as a simple TXT Record. A DMARC record lets domain admins announce their policies for unauthorized emails and receive reports on their outgoing email infrastructure.
What Is a DMARC Record Lookup Tool?
DMARC Record Checker is a free online DMARC diagnostic and lookup tool that allows you to verify and validate your domain's DMARC record, providing comprehensive DMARC verification. Simply enter your domain name, and the tool will retrieve the DMARC record and provide you with a comprehensive configuration analysis. With a DMARC lookup tool, you can quickly identify any issues with your DMARC record and take the necessary steps to ensure proper setup and compliance.
Why Check your DMARC record?
A DMARC lookup tool shows if the DMARC record exists and reveals existing issues. This helps to ensure that your business domain infrastructure is protected. If the DMARC Record Checker finds any problems, you can always turn to EasyDMARC’s platform and fix anything that hinders your domain-level security.
Why are DMARC reports important?
DMARC reports are key for successful DMARC enforcement (reaching to p=reject). They’re a data goldmine about your outgoing email ecosystem, showing legitimate and unauthorized sources, your email sending volume, and reasons for failing. Using this information, you can put together an action plan for swift DMARC enforcement and, ultimately, compliance.
What does DMARC compliant mean?
DMARC Compliance means that your outgoing email server is authenticated and aligned with either SPF or DKIM authentication protocols.
How does DMARC work?
In short, DMARC is an announcement on a domain’s DNS that states how the receiving servers should deal with emails from unauthorized sending sources. Here’s how it happens.
First, the domain admin implements a DMARC TXT Record in their DNS, mentioning the required and recommended tags like version, policy, and reporting. This sets the rule for receiving servers.
Receiving servers apply this added rule to all the emails from the given domain by reviewing SPF and DKIM authentication and alignment.
If the reporting tags RUA and RUF are in place, the domain administrator will start receiving DMARC reports. The next step is to dig into source alignment, gradually moving to a more strict policy by first implementing quarantine, then rejecting.
What does DMARC domain alignment mean?
Domain Alignment is the core DMARC concept. It ensures that the email address in the “From” header is the actual sender of the message. This means that the domain SPF check (which is based on “Envelope From:” or “Return-Path” address) and the DKIM signing domain (d=example.net) align with the message “From:” address.
How does a DMARC work with subdomains?
By default, DMARC Record or policy implemented on the root domain level will automatically apply on all subdomain levels, unless admins implement explicit DMARC Record on the subdomain(s) level.
Can I Add a DMARC Record Without DKIM?
Technically, you can add a DMARC record without having a DKIM record. However, for DMARC to pass, you need to have either SPF or DKIM authentication and alignment in place.
At EasyDMARC, we always advise our customers to start their DMARC journey by setting up both SPF and DKIM, and only then move on to DMARC.
Following email authentication best practices will ensure that you avoid false positive cases, lose or block legitimate emails, or damage your domain ecosystem in any way.


