DKIM Record Checker
EasyDMARC's DKIM validator is the easiest way to verify the digital signatures and integrity of incoming emails to prevent spoofing, phishing, and spam
Use EasyDMARC’s DKIM Record Check Tool to Find and Fix Email Authentication Issues
EasyDMARC's DKIM Checker tests and validates your domain’s DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) and makes sure it’s implemented correctly. Our DKIM Record Checker analyzes emails to confirm that they have been signed using the private key of a given domain and that the digital signature is valid. This helps domain owners take control of messages, confirming that each comes from the reported domain and has not been altered in transit.
Our DKIM Record Check can prove that a public record is associated with a given selector, uncovering issues in your DKIM record syntax before they impact your organization. Try EasyDMARC’s DKIM Lookup tool, and take the first step toward email authentication.
What is a DKIM Record?
- A DKIM record is a TXT-format DNS entry containing the selector and the public key used for email authentication. The selector identifies the specific private key used to sign the email message, while the public key is used to verify the signature of the email message.
Here is an example of a DKIM record:
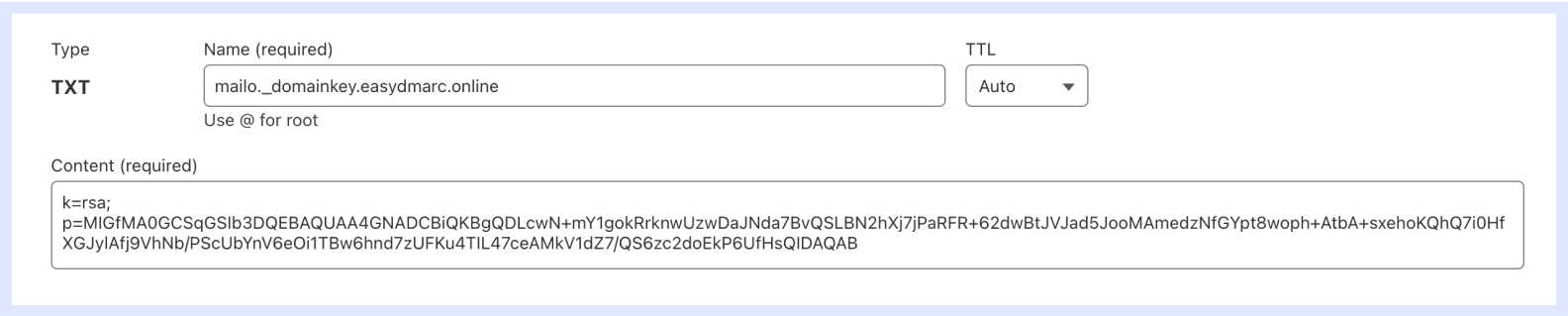
In this example, mailo is the selector prefix, and easydmarc.online is the domain name. The v=DKIM1 tag indicates that this is a DKIM record, k=rsa specifies that RSA encryption is used, and p= includes the public key for the domain.
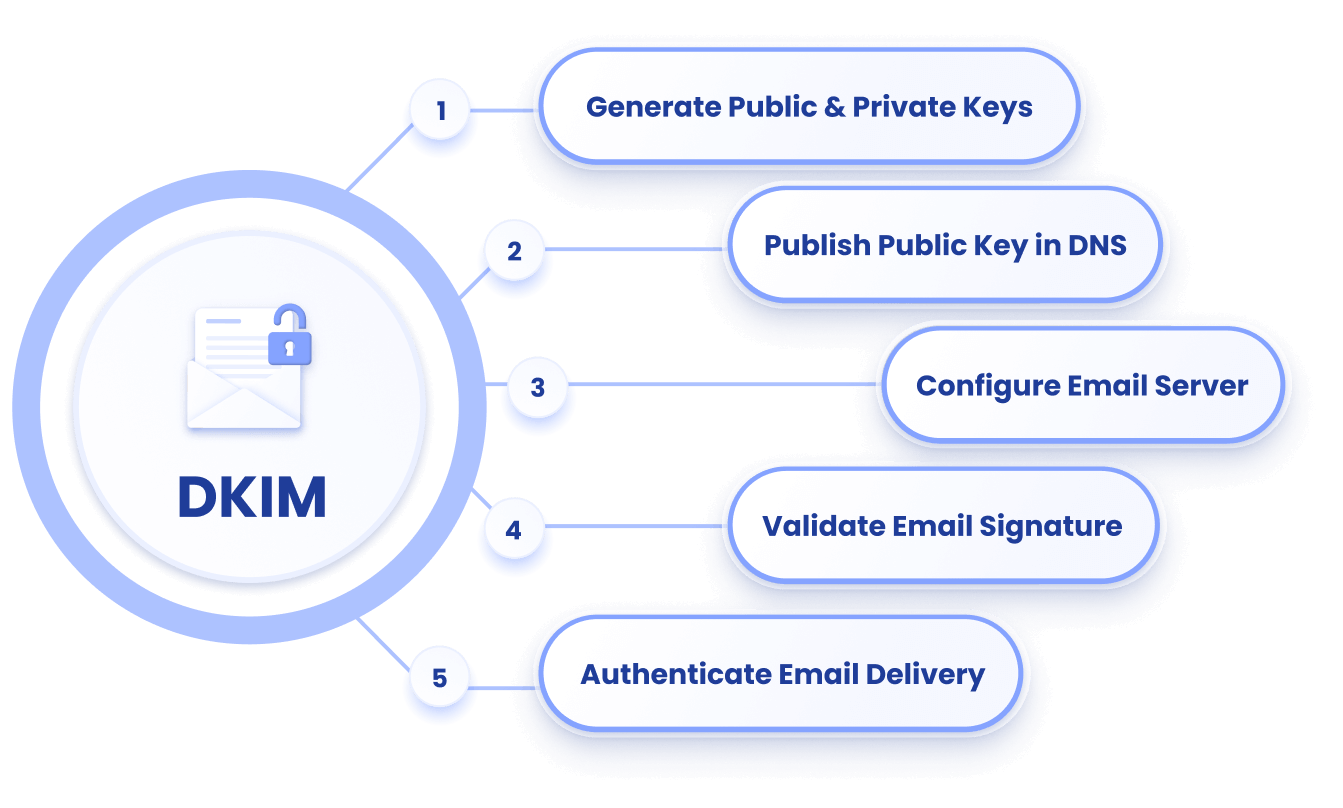
How Does DKIM Work?
When a recipient's email server receives an email message, it uses the public key from the sender's DNS record to validate the signature in the email header. If the signature is valid, the recipient can be confident that the email comes from the domain it claims to be from and that the contents of the email have not been tampered with in transit.
To use DKIM, a domain owner must create a public/private key pair, publish the public key in a DNS TXT record under the domain name, and configure their email server to sign outgoing messages using the private key.
However, third-party email service providers (ESPs) like Google, Microsoft, and SendGrid keep the private keys in their own servers without sharing them publicly. Here, the user must retrieve the Public Key from their portal or contact the provider's support team to obtain it. The recipient's mail server then queries the DNS to retrieve the public key and validate the signature in the email header to determine if the message is authentic.
What is a DKIM Record Check?
A DKIM record check is a process that verifies the authenticity of a domain's DKIM record. When an email is sent, the sender’s mail server signs the email with a private key. Upon receiving the email, the recipient’s server retrieves the corresponding DKIM record from the DNS using the selector. It then validates the signature in the email header with the public key.
When receiving an email, the recipient’s server retrieves the DKIM record from the DNS and uses it to verify its authenticity. The selector identifies the specific private key used to sign the email message, while the public key is used to verify the signature of the email message. If the DKIM check is successful, the email is confirmed as legitimate.
Why Use EasyDMARC for DKIM Record Checks?
Our DKIM checker tool simplifies the DKIM record-checking process by locating your domain's DKIM record and validating its accuracy. Our tool offers a unique advantage by automatically detecting DKIM keys using predefined selectors, streamlining the lookup process.
Unlike other DKIM lookup tools, we store DKIM keys from Aggregate Reports, allowing for automated lookups without the need for you to manually input selectors. This feature saves time and effort, ensuring that you can quickly verify your DKIM records.
Additionally, if any issues are detected with the selectors, our dashboard alerts you with clear warnings, helping you to proactively identify and resolve potential email authentication issues quicker.

EasyDMARC Has Everything You Need For Secure Servers
Explore EasyDMARC's free email authentication tools to enhance your domain's security and improve email deliverability. From verifying SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to analyzing reports, our tools provide actionable insights to safeguard your domain against spoofing and email fraud.
Here are some of our tools:
Why do you need DKIM, DMARC, and SPF checks?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance), and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) are all email authentication protocols that help prevent email spoofing and improve email deliverability.
Spammers and scammers use email spoofing to send fraudulent emails that appear to come from a legitimate sender. Email authentication protocols help prevent spoofing by allowing email service providers and recipients to verify that the message was sent by the domain owner or a legitimate sender authorized by the domain owner.
Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to:
- Improve email deliverability: Email service providers are more likely to deliver your emails to the intended recipient's inbox if they can verify that the email is legitimate.
- Protect against email spoofing and fraud: Email authentication can prevent unauthorized parties from using your domain to send fraudulent or malicious emails.
- Monitor and manage your email reputation: DMARC provides visibility into how your domain is being used for email and allows you to monitor and manage your domain reputation.
Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is crucial to ensure your domain is protected from email-borne attacks and that your email messages reach the intended recipients' inboxes.
Why does DKIM lookup matter?
DKIM record lookup matters because it gives you information on DKIM issues. Knowing the problems is the first and most crucial step before building your email authentication action plan.
What does DKIM lookup do?
EasyDMARC’s DKIM Checker:
- Checks if the DKIM TXT record is published in DNS for the domain
- Checks the published DKIM TXT record syntax
- Validates the DKIM public key associated with the selector
It also gives warning messages for each problem it finds in your DKIM record.
How to test DKIMkey?
Here's how to test DKIMkey in 4 steps:
- Check the email headers for the "DKIM-Signature" field, and verify the "d=" tag to ensure the email was signed using your domain's DKIM. Also, use the "Authentication-Results" field to check if the email passed or failed DKIM validation.
- Use EasyDMARC's DKIM checker tool to verify the syntax and configuration of your public key signature. We recommend sticking to one reliable DKIM checker tool to ensure consistency of results.
- Use EasyDMARC's Email Investigate tool to investigate specific email messages with DKIM issues. The tool provides DKIM pass or failure results that help identify if the DKIM is working. Still, it doesn't provide visibility into specific DKIM signature issues such as signature algorithm, public key, or signature itself.
- Monitor your DMARC Aggregate Reports daily to ensure your email authentication protocols, including DKIM, work as expected. Ensure your DKIM keys are correctly configured and published in your DNS records. If you notice any issues with your email authentication setup, take appropriate action to resolve them.
How to check DKIM via “nslookup” from the command line?
You can check the DKIM record for a domain using the nslookup command in the console or command line. Here's how:
- Open the console or command line on your computer.
- Type nslookup -q=txt <selector>._domainkey.<domain> where <selector> is the DKIM selector and <domain> is the domain name.
- Press Enter to execute the command.
- The output will display the DKIM record for the domain, including the public key and other information.
Below is an example of checking the DKIM record for the domain easydmarc.us with the selector google:
DKIM Record Value
nslookup -q=txt google._domainkey.easydmarc.us
Non-authoritative answer:
google._domainkey.easydmarc.us text = "v=DKIM1; k=rsa;
p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAtlOQQmjs3Y5diVg6cKpeJNfiWy0V9DXUERY3xvDyOC2DF8X2P+oNsNfuqpFdffsSMLxyQOe2aj2msqHaX6MoG8ATUfk1pnNhUu8gqphhyMeBOpGRBsDPCPmaLj+SxO42Tbo9jz8yV//zoTVIJlHe3VKe8DrE22kGT2GcdVQdTR2YLtEV8e4UEgT2pPVmRdpZ"
"PXYq/nESCaMi8JTCTaARjTpi2Nxs/G4eV8dSv7RIw0qXz6XDfNyDacJ6uIs1hC84R+tFX0GCMJ+z6heD6PPCZtDhBj/hy1MGwg3z+5izDBEBsgCRsNaVa0XHKb54I1L9f/x502WUN9dmOv41jPlswIDAQAB"
The command will return the DKIM record for google._domainkey.easydmarc.us, which includes the DKIM public key and other information.
How to check DKIM via the command line with the dig?
To check the DKIM record for a domain using the dig command, follow these steps:
- Open the console or command line on your computer.
- Type dig <selector>._domainkey.<domain> TXT where <selector> is the DKIM selector and <domain> is the domain name.
- Press Enter to execute the command.
- The output will display the DKIM record for the domain, including the public key and other information.
Here's how you can check the DKIM record for the domain easydmarc.us with the selector google:
DKIM Record Value
dig txt google._domainkey.easydmarc.us
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> txt google._domainkey.easydmarc.us
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 10094
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;google._domainkey.easydmarc.us. IN TXT
;; ANSWER SECTION:
google._domainkey.easydmarc.us. 300 IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAtlOQQmjs3Y5diVg6cKpeJNfiWy0V9DXUERY3xvDyOC2DF8X2P+oNsNfuqpFdffsSMLxyQOe2aj2msqHaX6MoG8ATUfk1pnNhUu8gqphhyMeBOpGRBsDPCPmaLj+SxO42Tbo9jz8yV//zoTVIJlHe3VKe8DrE22kGT2GcdVQdTR2YLtEV8e4UEgT2pPVmRdpZ"
"PXYq/nESCaMi8JTCTaARjTpi2Nxs/G4eV8dSv7RIw0qXz6XDfNyDacJ6uIs1hC84R+tFX0GCMJ+z6heD6PPCZtDhBj/hy1MGwg3z+5izDBEBsgCRsNaVa0XHKb54I1L9f/x502WUN9dmOv41jPlswIDAQAB"
The command returns the DKIM record for google._domainkey.easydmarc.us, which includes the DKIM public key and other information in the "ANSWER SECTION"
How to check DKIM record in your DNS?
Here’s what you need to do to check your DKIM record manually:
- Go to your DNS provider and log in
- Navigate to the records page and search for a TXT or CNAME type record with the Host / Name similar to the following string: [selector]._domainkey. yourdomain.com
This method gives the same result as inputting your domain and selector in our DKIM record checker tool.
How to analyze DKIM selector from email headers?
DKIM selector is inserted into the DKIM signature email header as an s= tag when the email is sent. Below is an example of a DKIM signature, where s= tag is what you’re searching for:
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa-sha256; c=relaxed/relaxed; d=easydmarc.com; h=content-type:from:mime-version:subject:reply-to:x-feedback-id:to: list-unsubscribe; s=s1;
How long does it take to set up DKIM?
The process of setting up DKIM depends on various factors, such as your level of familiarity with the process, the complexity of your email infrastructure, and the policies and procedures of your email service provider or hosting company.
The process of setting up DKIM involves the following:
- Generating a public and private key pair
- Publishing the public key as a DNS record
- Configuring your email server or service to sign outgoing messages with the private key
If you are using a third-party email service provider, such as Google Workspace or Microsoft 365, the DKIM setup process is usually straightforward and only takes a few minutes. Simply follow the provider's instructions.
If you're managing your own email infrastructure, DKIM setup may require more time and technical expertise. You need to generate the keys, publish the DNS record, and configure your mail server to use DKIM, which can take anywhere from a few hours to a few days, depending on your experience and the setup complexity.
It's worth noting that the time it takes to set up DKIM is only part of the process. After you've set up DKIM, you'll need to monitor its performance and make adjustments to ensure the optimal deliverability of your email messages.
What are some common DKIM issues?
- DNS configuration errors: DKIM requires the correct setup of specific DNS TXT records, including the DKIM public key and policy records. Any errors in the DNS configuration can cause DKIM to fail, for example, missing or incorrect records or syntax errors.
- Key length: The DKIM key length must be at least 1024 bits, but some email providers require longer keys. Using a key that is too short can result in DKIM failures.
- Mismatched domain names: DKIM requires that the domain name used in the DKIM signature matches the domain name used in the email's From address. If there is a mismatch, DKIM will fail. This process is also known as DKIM alignment, an essential factor for DMARC compliance.
- Incorrect signing algorithm: DKIM allows for several signing algorithms, but not all email providers support all of them. Using an unsupported algorithm can cause DKIM to fail.
- Message body changes: DKIM signs the email message headers and the body. Still, if you change the message body after it has been signed, the DKIM signature will become invalid. This can happen if the email passes through a gateway or is modified by a content filter. In this case, the DKIM signature will fail verification when received by the recipient's email server.


