AAAA Record Lookup
Perform a DNS AAAA Record lookup by entering your domain, IP address, and DNS server.
AAAA Record Lookup and IP6 DNS Lookup for your Infrastructure
Just as A record lookups can help you find which IPv4 Address is tied to your domain, a AAAA DNS record lookup can help you find which IPv6 Address is tied to your domain. Pronounced “Quad A” and increasingly common online, AAAA records are a vital part of your DNS.
IPv6 is a newer version of IP address and is increasingly prevalent as the internet grows and expands, meaning there is a good chance your DNS record lookup will include a AAAA record. These records are critical for the normal operation of your domain, as without them, the URL entered in a browser will not be able to find the IP address hosting your website.
IPv6 DNS lookups are an important part of DNS maintenance and are most commonly used when troubleshooting, during initial setup, and when migrating to new servers. With EasyDMARC’s AAAA DNS Lookup Tool, finding your domain’s records is easy, quick, and effective. Try it today for free.
The Different Types of DNS Records
EasyDMARC’s DNS lookup tool works for all types of DNS records. Knowing what each of these records do and how to manage them is essential for running an efficient and effective DNS for your domain.
- A Records map your domain to an IPv4 address.
- AAAA Records map your domain to an IPv6 address.
- MX Records directs email to a mail server rather than an IP address.
- CNAME Records create an alias for additional domains.
- TXT Records stores text for the purpose of verification and authentication.
- PTR Records are used when looking up a domain with an IP address.
- NS Records show the authoritative domain name servers.
- SOA Records contain DNS zone details.
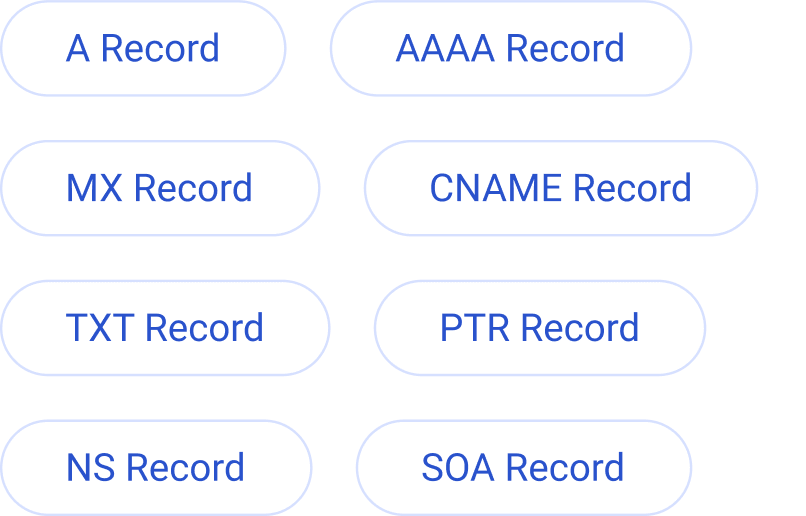
How EasyDMARC’s DNS AAAA Record Lookup Works
Looking up and checking your AAAA records with EasyDMARC’s lookup tool is quick and easy. Follow these simple steps:
- Enter your domain or IP – Input your domain name or the IP address hosting it.
- Choose a DNS server – Select a DNS host from popular options like Google, Cloudflare, Quad9, or your domain’s SOA.
- Review your DNS records – EasyDMARC presents your DNS files in a well-organized, easy-to-understand list. Click a record for more details.
Where can I find the AAAA Record?
You can find your AAAA records in your DNS provider’s dashboard, through your domain registrar's DNS settings, or using online tools like EasyDMARC’s AAAA Record lookup.
How to Perform an IPv6 DNS Lookup
You can perform an IPv6 DNS lookup to find a domain's AAAA record by using online tools like EasyDMARC, but you can also find them through your computer’s Command Prompt or Terminal applications.
For Terminal (on MacOS and Linux), type in “dig AAAA example.com” where the URL is your domain.
For Command Prompt (on Windows) type in “nslookup -type=AAAA example.com” where the URL is your domain.
How to Remove a AAAA Record?
To remove a AAAA record (IPv6) from your domain:
- Log in to your DNS provider and navigate to where your domain's DNS is managed.
- Open DNS or Zone Editor and look for a section called DNS settings, DNS management, or Zone Editor.
- Find the AAAA record in question. It should be linked to your domain or subdomain.
- Delete the record by clicking delete, a trash icon, or similar next to the AAAA record.
- Save changes and make sure to click “Apply changes” if needed. DNS changes may take a few minutes to propagate.
Is IPv6 Faster than IPv4?
IPv6 can be faster, but it depends on your network, ISP, and the websites you're accessing.
When IPv6 can be faster:
- No NAT (Network Address Translation) – IPv6 allows direct connections, which can reduce latency.
- More efficient routing – Some networks are optimized for IPv6 paths.
- Preferred by modern systems – Devices and apps may default to IPv6 if available.
When IPv4 may be faster:
- Network not optimized for IPv6 – If your ISP or website has poor IPv6 support, performance may drop.
- Caching and infrastructure – IPv4 has more mature optimization in some areas.


