SOA Record Lookup
Check your domain’s SOA records in seconds. Enter your domain or IP address to get started for free.
Check DNS SOA Records for Your Infrastructure
SOA records, or Start of Authority records, are used to define important administration information for a domain. They identify which DNS server is the authoritative source for information about your domain. They are also used when synchronizing DNS data between primary and backup DNS servers. In essence, they manage how DNS data is distributed, synchronized, and maintained across the internet. They're foundational to the stability and proper functioning of domain name resolution.
If you are implementing changes to your DNS, investigating propagation delays, setting up secondary DNS servers, or reviewing security and compliance, using an SOA checker is essential. Try EasyDMARC’s DNS SOA Record Lookup tool for free.
When to use DNS Lookup Tools
EasyDMARC’s all-in-one DNS Record Lookup tool can look up and detail any DNS record for your domain. Knowing what these records do for your domain is essential for running a properly configured domain.
- A Records – Ties an IP address to a domain name
- AAAA Records – Same as an A record, except it uses IPv6 addresses
- MX Records – Used to direct email to mail servers
- CNAME Records – Makes an alias for other domains, similar to a redirect
- TXT Records – Contains important text records for verification and policies
- PTR Records – Used during reverse DNS lookups
- NS Records – Identifies the authoritative name servers
- SOA Records – Lists important DNS zone information
With EasyDMARC’s DNS Record lookup tool, you can ensure your domain is properly configured for smooth domain operations.
How to Use EasyDMARC’s SOA Record Lookup Tool
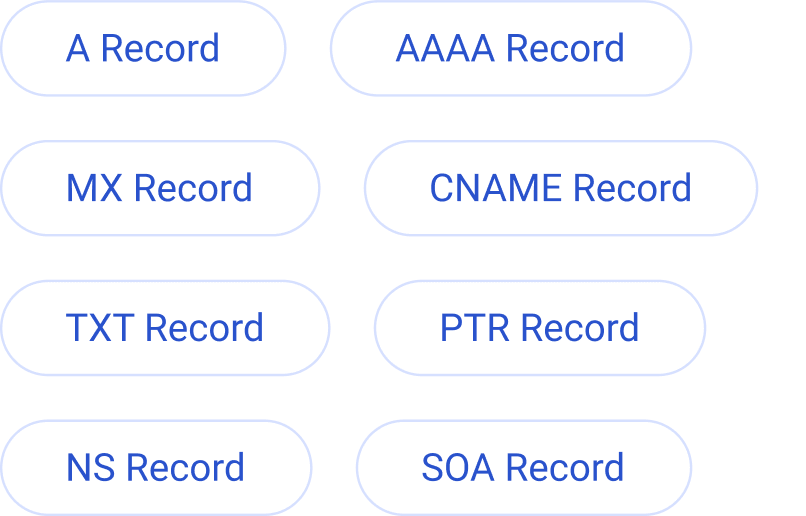
Finding and checking your SOA records is fast, free, and easy with EasyDMARC’s DNS SOA Lookup. Follow these simple steps:
- Enter your IP address or domain
- Choose a DNS server
- Browse your records or click one for more details
Our tool shows your domain’s DNS records in a simple, organized list to help you quickly understand your DNS configuration. Try it for free today.
What is SOA in DNS Lookup?
In a DNS lookup, SOA stands for Start of Authority. It’s a special type of DNS record that provides administrative details about a domain’s DNS zone. It’s always the first record in a DNS zone file. An SOA record includes:
- Primary authoritative nameserver for the domain
- Email address of the domain administrator
- Serial number (used by secondary servers to know whether the zone has been updated)
- Refresh time (how often secondaries check for updates)
- Retry time (how soon to retry if a refresh fails)
- Expire time (how long secondaries serve data without updates)
- Minimum TTL (default caching time for other DNS resolvers)
How do I find my SOA?
You can find your domain’s SOA (Start of Authority) record using simple DNS lookup tools.
For Windows, open Command Prompt and type, without quotation marks, “nslookup set type=soa yourdomain.com”
For Linux and MacOS, open Terminal and type, without quotation marks, “dig soa yourdomain.com”
The easier method is to use online tools like EasyDMARC’s DNS record lookup tool. Simply enter your domain name or IP address, then enter your domain server, and click “find records.”
How to get a SOA serial number?
You can get your SOA serial number by performing a DNS SOA record lookup.
For Windows:
- Open Command Prompt
- Type:
- nslookup
- Set type=soa
- yourdomain.com
For MacOS or Linux:
- Open Terminal
- Type:
- Dig +short soa yourdomain.com
An example of the type of output you should expect:
ns1.example.com. hostmaster.example.com. 2025052301 3600 600 1209600 3600
What is the recommended value for DNS SOA?
There isn’t a single “recommended value” for a DNS SOA record as a whole, but each field within the SOA record has recommended ranges depending on your DNS setup and how frequently your zone data changes.
Recommended values for each field:
| Field | Recommended Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Serial | YYYYMMDDnn format | Incremental when you update DNS records |
| Refresh | 3600 (1 hour) | How often secondary DNS checks for updates |
| Retry | 600 (10 minutes) | Wait time before retrying a failed update |
| Expire | 1209600 (14 days) | How long secondaries serve if primary is down |
| Minimum TTL | 3600 (1 hour) | Default TTL for negative responses |
What happens if there is no SOA record?
If there is no SOA (Start of Authority) record for a domain, the DNS zone is considered invalid and will not function properly. Without an SOA record, DNS servers cannot validate the zone, and many will refuse to load or serve it. This means secondary DNS servers cannot perform zone transfers because they rely on the SOA’s serial number to determine whether updates are needed. DNS propagation across servers will fail, potentially making the domain unreachable.
DNS troubleshooting tools, such as dig or nslookup, also rely on the SOA record to identify authoritative nameservers and verify DNS status. Without it, these tools may return incomplete or misleading results, which can complicate diagnostics. In short, the absence of an SOA record breaks the foundation of how DNS zones operate, and it should be corrected immediately to ensure proper domain resolution.


