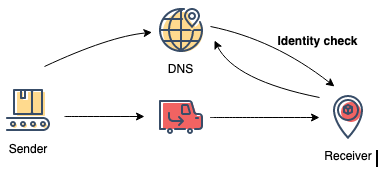
If you have a business domain, there’s a chance that you’ve heard techie terms like email security, DNS, and protocols. But what are those terms and what’s email authentication?
Let’s start at the beginning. The chances are that during the business domain setup, you created email addresses with your business domain name at the end. This is a custom company email address that belongs and is managed by you. While you’re the owner of this communication platform, it’s still unprotected, as emails are simple text files and can be hijacked by bad actors, forged, and misused. Enter email authentication protocols that let you verify and protect your communication. In a nutshell, email authentication is a way to tell mail services that you’re the real deal, your emails are legitimate, and that your emails absolutely belong to inboxes.
How Does Email Authentication Work?
To make email authentication work, you need to create and maintain special DNS records (rules of sort), which would guide Email Service Providers (ESPs) and give them information about whether the communication is legitimate, whether you’re the sender or not, or if the original message was altered.
When your identity can easily be verified, it is much harder for cybercriminals to “spoof” your domain and send emails that look like they came from you. Sending a fake email, usually containing malicious links, on behalf of others is also known as a phishing attack. Phishing emails are one of the most common and dangerous attacks worldwide.
On top of the said above, email authentication also
- Cuts down on spam
- Improves your email deliverability
- Improves your domain reputation
- Maintains your brand authenticity
What are the Mechanisms of Email Authentication?
There are 3 key components in email authentication that businesses can set up so that ESPs can verify their identity and legitimacy:
- SPF
- DKIM
- DMARC
Now that you know what email authentication is and how it protects your corporate email let’s go through its components.
What is SPF in Email Authentication?
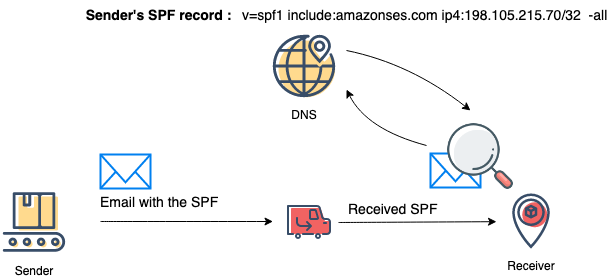
SPF, or “Sender Policy Framework,” is the first component of email authentication. It’s a verification mechanism between the sender and the receiver that verifies the legitimacy of the sending source. This mechanism prevents spammers from using your domain to send fraudulent emails.
Let’s briefly go through how SPF works in the email authentication process:
Step 1. The sender publishes the list of authorized sources (IPs or 3rd party servers) in the domain DNS.
Step 2. Upon receiving the email, the Receiver makes a request to the Sender’s domain DNS to retrieve the list of authorized sources.
Step 3. Receiver checks if the Sender’s IP address is in the published sources list.
Step 4. Depending on the success or failure of sources check the relevant policy is being applied.
SPF Policies
SPF has 4 policies which are applied through the following “qualifiers”:
- + pass
- – fail
- ~ softfail
- ? neutral
You can find more about SPF in RFC.
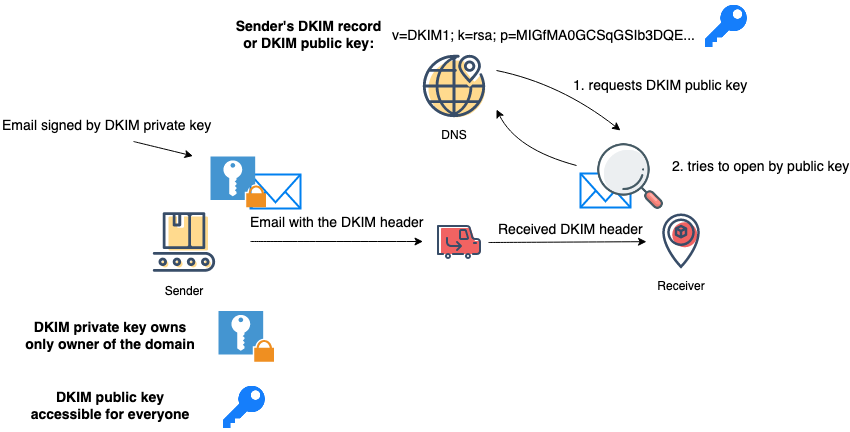
How Does DKIM Work?
DKIM, or “DomainKeys Identified Mail,” is a digital signature embedded in the Sender’s email header. The Receiver’s Mail Servers can check it to determine if the received email indeed originated from the right sender and has not been tampered with on its way. Note that this isn’t something that your email recipient customer, partner, or employee will see, and you can adjust the “send as” name that appears in the inbox. However, the recipient ESP or mail server will be able to see that your domain is reputable.
The process of picture 3 in detail:
Step 1. The Sender generates DKIM keys (public and private) and publishes the public key in the domain DNS.
Step 2. Sender signs email using DKIM private key, which is tied to the domain owner itself.
Step 3. The Receiver looks up for DKIM public key in Sender’s domain DNS.
Step 4. The Receiver verifies the digital signature using the public key retrieved from DNS. Successful verification means that the received email came from a genuine sender.
You can find more about DKIM in RFC
Why Use DMARC?
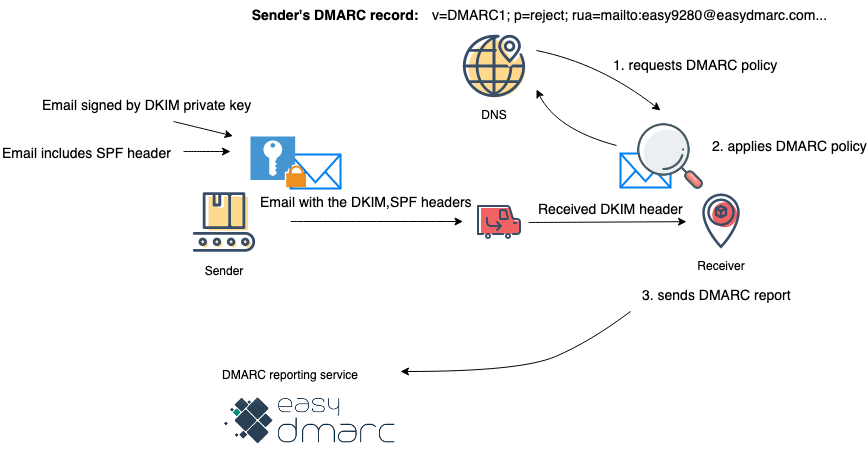
The third component of email authentication is DMARC. DMARC is an acronym for “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance.” If either the sender or recipient uses DMARC, it requires that the email sender uses either SPF or DKIM to verify their identity. What’s more, when it’s configured properly, DMARC can pass or reject emails based on their identity check. You can think of DMARC like running a background check on an email’s sender before it is put through to your inbox.
There are some added benefits to using a DMARC protocol:
- It adds a level of security above and beyond either SPF or DKIM.
- DMARC works in conjunction with SPF and DKIM, but when used in a monitoring mode, it can work on its own.
Note that if your goal is to run a strict DMARC security policy than SPF and DKIM are mandatory.
- Your reputation may increase simply by enacting DMARC. This shows ESPs (and their customers) that you care about your reputation.
- More of your emails are delivered straight to the inbox.
DMARC works as simple as
Step 1. The Receiver requests DMARC policy.
Step 2. Applies DMARC policy based on response to SPF and DKIM checks.
You can find more about DMARC in RFC.
What Happens In Case of Missing Email Authentication?
In a perfect world, nothing happens. However, the reality is that cybercriminals are constantly probing for ways to drop infected links and emails to your inbox as well as your customers. So if you don’t put any email authentication practices into action, people can impersonate you and your business, leading to fraud and phishing attacks.
Two points we would like to stress:
- The FBI estimates the average loss from phishing attacks is around 1.6 million U.S. dollars for mid-size companies
- The other worst-case scenario is that ISPs may block or blacklist your domain, which can be time-consuming and costly to resolve
So it is strongly recommended to have properly configured email authentication to protect your domain from cybercriminals, and to protect your valuable brand from a drastic loss in reputation.
Email Authentication: Set and Forget?
Although email authentication is difficult to set up and requires intelligent forethought, the reality is that it’s not something that you can set and forget. Instead, you’ll want to stay on top of what kinds of emails are being sent, who is sending them, and what percentage are reaching client inboxes. You want to stay proactive and routinely monitor
Using a service like EasyDMARC can help you manage your email authentication, protect your data, and actively monitor for any improper or uncommon uses of your email. With Smart Alerts and Notifications about attacks and infrastructure changes, you’ll be able to rest easily. You’ll feel secure knowing that your emails are landing in the right inboxes and that if someone does manage to fraudulently spoof your emails, the problem will be handled before it does lasting damage to you, your employees, or your customers.
The Bottom Line: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Are Mandatory
Well, not exactly, but… Email authentication is highly recommended in today’s business world. Your business has many customers, and it likely deals with personal data. Email can be one of the most vulnerable paths to exposing that information. Ignoring email authentication is like not using a password on your work laptop.
Moreover, email authentication needs constant monitoring if you want to harness its full potential. EasyDMARC’s platform helps keep an eye on any changes to your server or senders, no matter how small.
When your emails don’t land in your client’s inboxes, your business loses out big time in lots of ways:
- Clients expecting an email may lose trust
- You lose potential sales if your marketing emails aren’t landing
- Top-of-mind awareness decreases when you aren’t visible
- The more time you ignore email authentication, the more time and money it costs to fix
- Above all, you can have big profit and reputation loss because of phishing attacks
You can find other tools and suggestions for email deliverability here.
The list of costs goes on and on. However, the solution is an easy one: put solid email authentication practices into play and then monitor them regularly. If time is a factor and you simply can’t stay on top of the data, start working with a service like EasyDMARC to help you prevent phishing and fraud and maintain your client’s trust and reputation.